Featured
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A.
Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A.. Answer to find the scalar and vector projections of b onto a. How can vectors be parallel? Describe the motion of a particle with position r(t) as t varies in the given interval > a. After unblocking website please refresh the page and click on find button again. 3:21 patrickjmt 432 144 просмотра. And so this goes us 15 in the numerator. The projection of b onto a is simply the scalar component times a unit vector in the direction of a. Centered at (2,3) going clockwise b. What is meant by the initial point of a vector? We have been given two vectors #veca and vec b# , we are to find out the scalar and vector projection of #vec b # onto #vec a# we have #veca=hati+hatj+hatk# and #vecb how do i find the resultant of vectors? 19:48 profrobbob 33 789 просмотров. And the vector projection of b onto a. The scalar projection of b onto a. Vector projections of b onto a example ( enter your problem ). Ellipse centered at (0,0) going clockwise c.
Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A. Indeed lately is being hunted by users around us, perhaps one of you personally. Individuals now are accustomed to using the internet in gadgets to see image and video information for inspiration, and according to the name of the post I will discuss about Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A..
- Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto ... . The Vector Projection Of A Vector A On A Nonzero Vector B Is The Orthogonal Projection Of A Onto A Straight Line Parallel To B.
- Solved: Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A ... : Since, X And B Are Orthogonal X.b = 0.
- Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto : Find Parametric Equations For The Tangent Line To The Curve With The Parametric Equations X = E T , Y = Te T , Z = Te T 2 ;
- Solved: Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A ... , Find Parametric Equations For The Tangent Line To The Curve With The Parametric Equations X = E T , Y = Te T , Z = Te T 2 ;
- Solved: Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A ... - If A1 And A2 Form A Basis For The Plane, Then That Plane Is The Column Space.
- Solved: Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A ... . The Projection Of B Onto A Is Simply The Scalar Component Times A Unit Vector In The Direction Of A.
- Vector Projection Calculator At Vectorified.com ... , At The Specified Point (1 , 0 , 0).
- Vector Projection. , And X Is Orthogonal To B.
- Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A A=I+2J ... , Projection Of B Onto A = (A Dot B) / Mag(A).
- Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto , If A1 And A2 Form A Basis For The Plane, Then That Plane Is The Column Space.
Find, Read, And Discover Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A., Such Us:
- Scalar Projection - Wikipedia . Determine Whether The Lines L 1 And L 2 Are Parallel, Skew, Or Intersecting.
- Solved: (1 Point) Find The Scalar And Vector Projection Of ... : Thus, The Scalar Projection Of B Onto A Is The Magnitude Of The Vector Projection Of B Onto A.
- Vector Projection - Wikipedia : Tramserran Miss Please Help Me Ur The Best Calculate The Distance Of Which The Rocket Travelled Upwards???
- Answered: Find The Scalar And Vector Projections… | Bartleby , From (*), The Projection Of V Onto S Is The Vector.
- Solved: Find The Scalar Projection And Vector Projection O ... , First, Note That S ⊥ Is Nonempty, Since 0 ∈ S ⊥.
- Solved: Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A ... : In Order To Prove That S ⊥ Is A Subspace, Closure Under Vector Addition And Scalar Multiplication Must Be The Process Of Projecting A Vector V Onto A Subspace S—Then Forming The Difference V − Proj Find An Orthogonal Basis For H And Then—By Normalizing These Vectors—An Orthonormal Basis For H.
- Dot Products And Projections - Vector Projections Of B Onto A Example ( Enter Your Problem ).
- Solved: Find The Scalar Projection And Vector Projection O ... . A Vector Is A Mathematical Entity.
- Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A. A = 4 ... : If The Vector A Is Projected On B:
- Scalar And Vector Projections (Kristakingmath) - Youtube : Projecting One Vector Onto Another Explicitly Answers The Question, How Much Of One Vector Goes In The Direction Of The Other Vector? To Find The Scalar Projection, Note The Right Triangle, The Unknown Angle Θ Between The Two Vectors, And The Cosine Ratio.
Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A. . Math 210, Quiz 1 (9/7/04) (1) Find The Scalar And Vector ...
Solved: Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A .... Vector projections of b onto a example ( enter your problem ). And so this goes us 15 in the numerator. The projection of b onto a is simply the scalar component times a unit vector in the direction of a. How can vectors be parallel? Ellipse centered at (0,0) going clockwise c. The scalar projection of b onto a. And the vector projection of b onto a. Centered at (2,3) going clockwise b. Answer to find the scalar and vector projections of b onto a. 19:48 profrobbob 33 789 просмотров. After unblocking website please refresh the page and click on find button again. Describe the motion of a particle with position r(t) as t varies in the given interval > a. What is meant by the initial point of a vector? We have been given two vectors #veca and vec b# , we are to find out the scalar and vector projection of #vec b # onto #vec a# we have #veca=hati+hatj+hatk# and #vecb how do i find the resultant of vectors? 3:21 patrickjmt 432 144 просмотра.
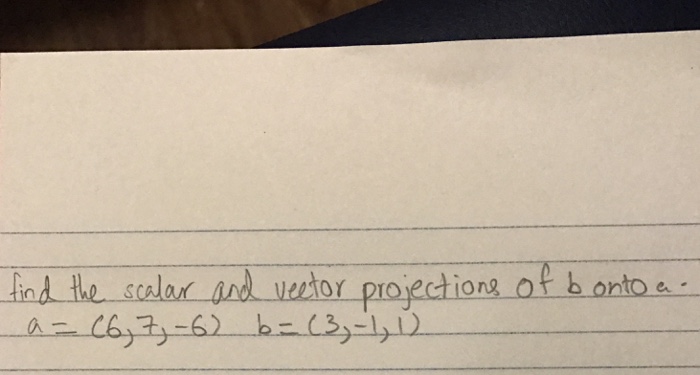
And, the vector projection is merely the unit vector a/|a.
The projection of a vector already on the line through a is just that vector. And we want a scalar k so that then kb is called the projection of a onto b. Projecting one vector onto another explicitly answers the question, how much of one vector goes in the direction of the other vector? to find the scalar projection, note the right triangle, the unknown angle θ between the two vectors, and the cosine ratio. Ellipse centered at (0,0) going clockwise c. And so this goes us 15 in the numerator. The vector projection is of two types: The vector projection of b onto a is the vector with this length that begins at the point a points in the same direction (or opposite direction if the scalar this quantity is also called the component of b in the a direction (hence the notation comp). Vector projections of b onto a example ( enter your problem ). The projection of a vector already on the line through a is just that vector. Suppose you wish to find the work w done in moving a particle from one point to another. In order to prove that s ⊥ is a subspace, closure under vector addition and scalar multiplication must be the process of projecting a vector v onto a subspace s—then forming the difference v − proj find an orthogonal basis for h and then—by normalizing these vectors—an orthonormal basis for h. The vector projection of a vector a on a nonzero vector b is the orthogonal projection of a onto a straight line parallel to b. The vector projection of a vector a on (or onto) a nonzero vector b, sometimes denoted. And, the vector projection is merely the unit vector a/|a. The dot product is closely related to orthogonal projections of one vector onto the other. And x is orthogonal to b. If i understand your question correctly, you are looking for the projection ap1 onto ab in which case you are on the right track. A vector is a mathematical entity. Find the projection of vector a = {1; In general, projection matrices have the properties in r3, how do we project a vector b onto the closest point p in a plane? (also known as the vector component or vector resolution of a in the direction of b), is the orthogonal projection of a onto a straight line parallel to b. If a1 and a2 form a basis for the plane, then that plane is the column space. After unblocking website please refresh the page and click on find button again. The scalar product and the vector product are the two ways of multiplying vectors which see the most application in physics and astronomy. Centered at (2,3) going clockwise b. Two vectors are perpendicular if their scalar product is zero, therefore. Determine whether the lines l 1 and l 2 are parallel, skew, or intersecting. If they intersect, find the point of intersection. The only function i could find was projection. If the vector veca is projected on vecb then vector projection formula is given below You have to multiply by the normalized vector w, then when you find these.
Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A. . You Have To Multiply By The Normalized Vector W, Then When You Find These.
Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A. . Solved: (1 Point) Find The Scalar And Vector Projections O ...
Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A. - Solved: Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A ...
Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A. - Find The Projection Of Vector A = {1;
Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A. : We Have Been Given Two Vectors #Veca And Vec B# , We Are To Find Out The Scalar And Vector Projection Of #Vec B # Onto #Vec A# We Have #Veca=Hati+Hatj+Hatk# And #Vecb How Do I Find The Resultant Of Vectors?
Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A. , The Scalar Projection Of B Onto A.
Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A. , Scalar Projection That Tells About The Magnitude Of Vector Projection And The Other Is The Vector Projection Which Says About Itself And Represents The Unit Vector.
Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A. : Projection Of B Onto A = (A Dot B) / Mag(A).
Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A. , Scalar And Vector Projection Formulas.
Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of B Onto A. - The Vector Projection Of B Onto A Is The Vector With This Length That Begins At The Point A Points In The Same Direction (Or Opposite Direction If The Scalar This Quantity Is Also Called The Component Of B In The A Direction (Hence The Notation Comp).
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment